 亚专科
亚专科

纳入2002年至2019年所有确诊为缺氧性脑损伤的患者。在ASL上绘制12个ROIs(感兴趣区),并在DWI上识别出与ASL坐标匹配的ROIs。采用线性回归分析探讨动脉自旋标记灌注与扩散信号的关系。使用custom-built algorithm 算法生成标准化弥散-灌注比图。
研究中纳入35例缺氧性脑损伤患者和34例健康志愿者。线性回归分析表明,ASL与DWI信号呈显著正相关。通过斜率截点范围组合>0和R2>0.78,使用ASL和DWI的线性回归分析显示,对缺氧脑损伤的敏感性为0.86 (95% CI 0.71-0.94),特异性为0.82 (95% CI 0.66-0.92)。NDP(标准化弥散-灌注彩色图)显示,在健康对照者中NDP表现出全脑分布不均匀,而缺氧脑损伤患者的NDP分布均匀。
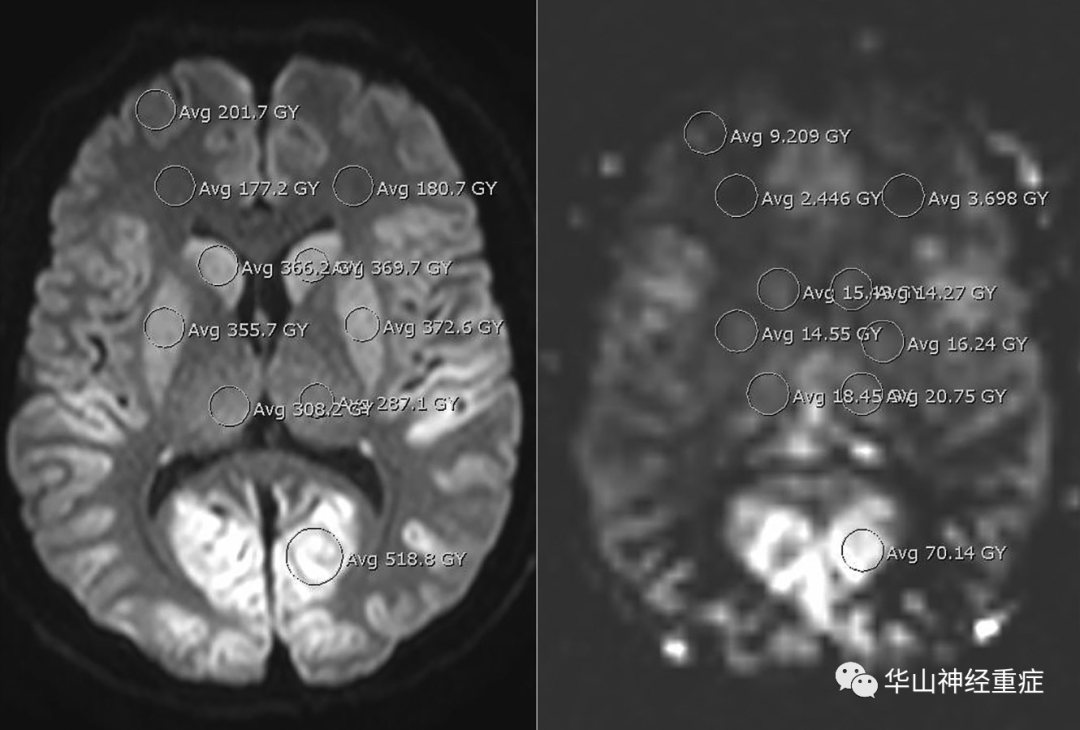
FIG 1. Sample image showing 10 of the 12 ROI measurements on DWI (left) and ASL (right) at the level of the basal ganglia in a patient who had anoxic brain injury.
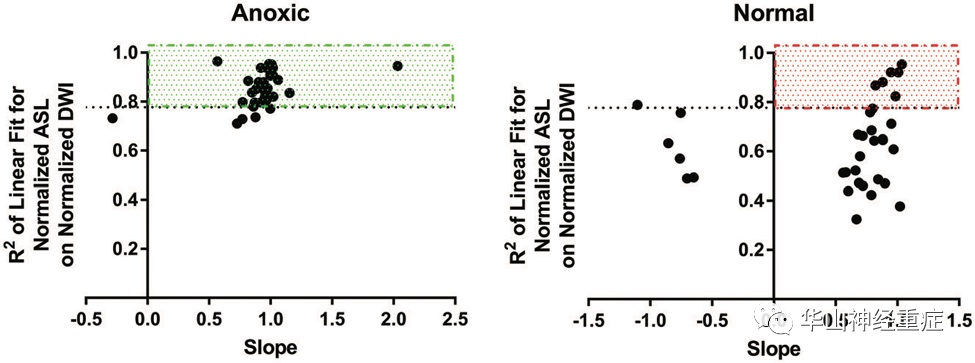
FIG 2. Twelve-point ROI linear regression analysis using DWI and ASL sequences.
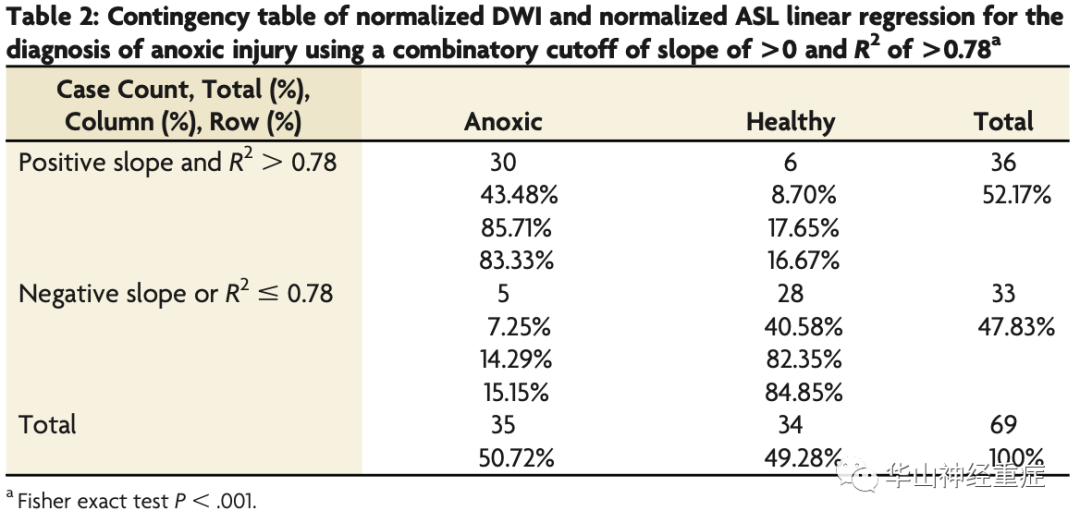
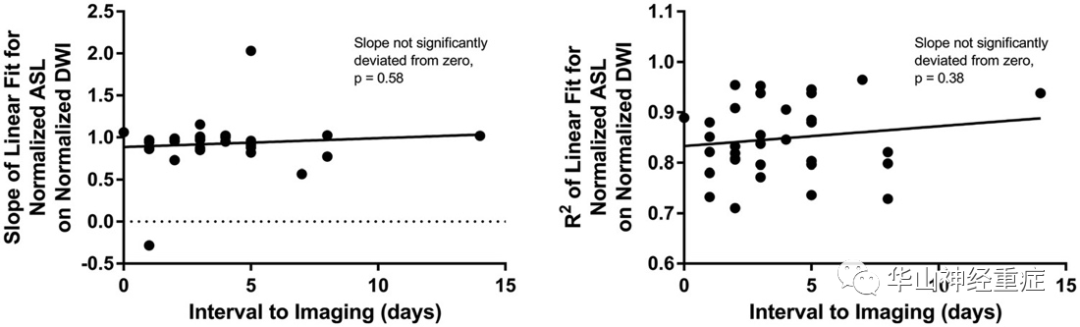
FIG 3. Linear regression analysis demonstrates no significant linear dependence between slopes and interval to imaging (left) or between R2 and interval to imaging (right), using DWI and the ASL sequences.
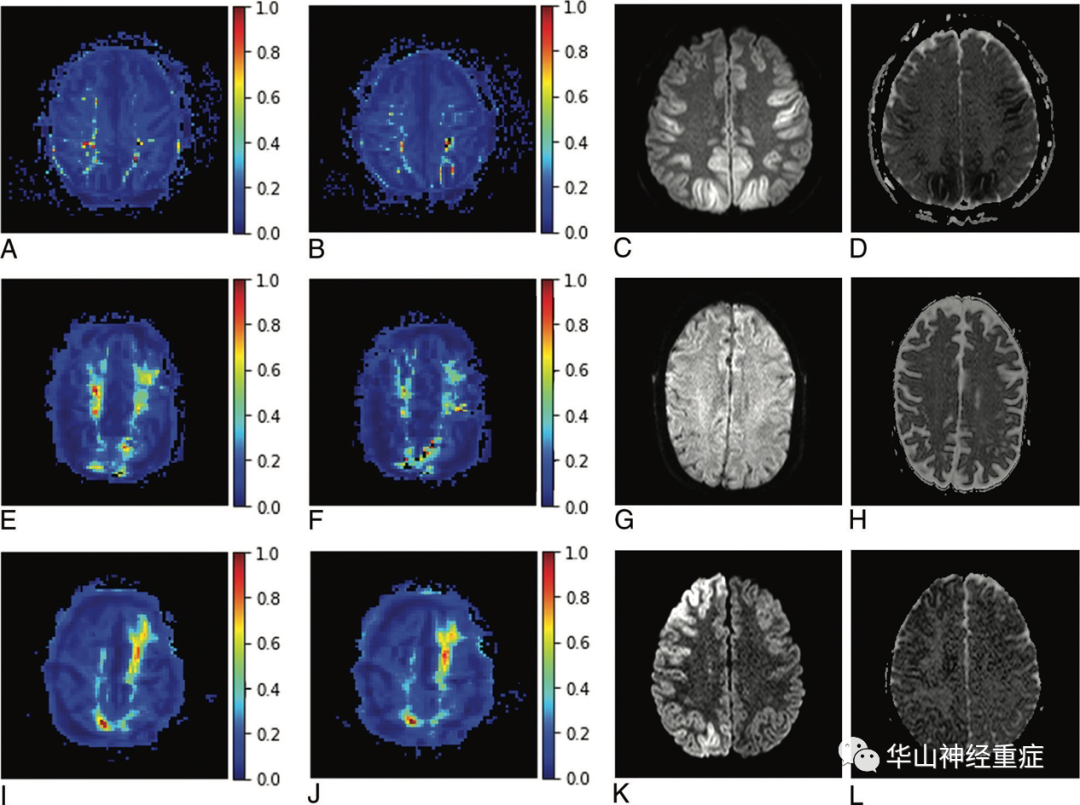
FIG 4. Representative slices of voxelwise normalized NDP color map generation and corresponding DWI and ADC images.
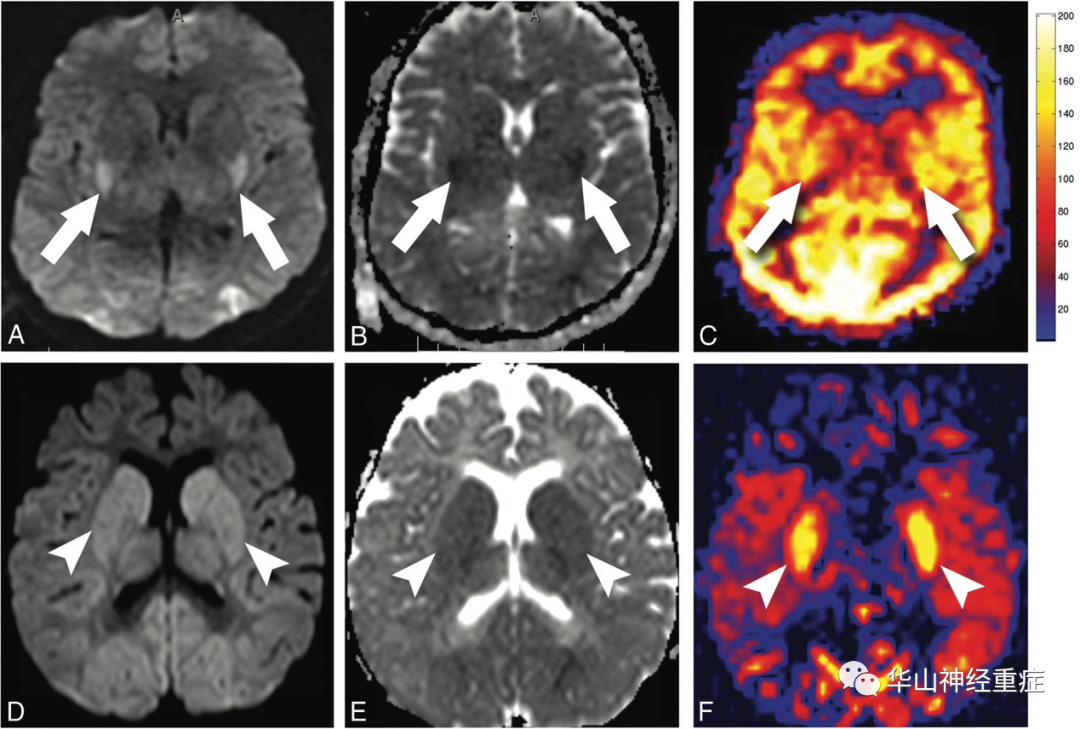
FIG 5. Quantitative-versus-nonquantitative ASL perfusion in anoxic brain injury.
讨论和阅读体会 |
对35例缺氧性脑损伤患者进行回顾性分析,发现典型的弥散限制性表现(DWI高信号,ADC低信号)。脑内代谢活跃的组织,尤其是基底节、丘脑腹外侧部、丘脑等部位的脑缺血改变(包括能量代谢变化和细胞毒性水肿)明显,大脑皮质除了先前定量ASL研究中发现的整体高灌注模式(图5A-C),对定性ASL灌注图像的回顾研究也表明DWI增强区域信号增加。因此将NDP(标准化弥散-灌注比)彩色图应用于诊断缺氧性脑损,可能为临床提前干预、治疗提供依据。
